java基础demo
java基础demo
记录基础学习时写的demo,复习基础
helloworld
package com.yuy0ung.test01;
/**
* @author Yuy0ung
*/
public class HelloWorld4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("hello world");
System.out.println("hello world");
}
}
变量
package com.yuy0ung.test01;
public class TestVar {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//定义年龄变量
int age;
//同时定义多个
int a,b;
//赋值
age = 18;
age = 19;
age = 18 + 19;
//变量定义+赋值
int age1 = 19;
int age2 = 18,age3 = 20;
int age4,age5 = 30;//这里age5被赋值但age4没有
//变量使用
System.out.println(age);
System.out.println(age+10);
System.out.println(age+age3);
}
}
基本数据类型
package com.yuy0ung.test01;
public class TestType {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//整数
byte a = 10;//-128~127
short b = 20;//正负3w
int c = 30;//正负21亿
long d = 4000000L;///大得很...(超过int范围加L)
//浮点
float e = 3.14f;//结尾要f
double f = 3.14;
//字符
char g = 'Y';//单引号括起来的单个字符
System.out.println("Yuy0ung");//字符串是多个字符拼接
//布尔
boolean h = true;
}
}
算术运算符
package com.yuy0ung.test01;
public class TestOpe {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(+10);
System.out.println(1+2);
int num = 10;
//从左到右运算,包括类型
System.out.println("这是一个数"+num);
System.out.println(500+20+"Yuy0ung");
System.out.println("Yuy0ung"+5+20);
num++;//自增
int a = 0;
++a;//自增
System.out.println(num);
System.out.println(a);
int b = 0;
int c = 0;
System.out.println(b++);//先运算后自增
System.out.println(b);
System.out.println(++c);//先自增后运算
}
}
赋值运算符
package com.yuy0ung.test01;
public class TestOpe2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//赋值
int num1 = 1;
int num2 = 2;
int num3 = 10 + 30;
//求和
int sum = 0;
sum = sum + num1;
sum = sum + num2;
sum += num3;
System.out.println("和:" + sum);
}
}
关系运算符
package com.yuy0ung.test01;
public class TestOpe3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//关系运算符
System.out.println(1 == 2);
System.out.println(1 == 1);
//逻辑运算符
System.out.println(true&&true);
System.out.println(true&&false);
System.out.println(false&&false);
System.out.println(false&&true);
System.out.println(false||false);
System.out.println(true||true);
System.out.println(true||false);
}
}
流程控制
if
package com.yuy0ung.test02;
public class TestIf01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int num = 18;
if (num > 10) {
System.out.println("大于10");
}
if (num < 10) {
System.out.println("小于10");
}
else {
System.out.println("大于10");
}
if (num < 18) {
System.out.println("小于18");
} else if (num > 18) {
System.out.println("大于18");
} else {
System.out.println("等于18");
}
}
}
while
package com.yuy0ung.test02;
public class TestWhile {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i = 1;
while (i < 10) {
i++;
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}
for
package com.yuy0ung.test02;
public class TestFor {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 10;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
System.out.println(a);
}
}
}
方法&重载
package com.yuy0ung.test04;
public class TestMethod {
//提取一个方法,用于求和
public static int addNum(int a, int b) {
int c = a + b;
return c;
}
//方法重载,方法名相同,形参列表不同
public static void addNum(int a, int b, int c) {
System.out.println(a+b+c);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int sum = addNum(1, 2);
System.out.println(sum);
System.out.println(addNum(4, 5));
addNum(6, 7,8);
}
}
数组
package com.yuy0ung.test05;
public class TestArray {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//int 为例
int[] arr;//定义
arr = new int[4];//创建长度为四
//创建后有默认值0
//赋值
arr[0] = 1;
arr[1] = 2;
arr[2] = 3;
arr[3] = 4;
//使用
System.out.println(arr[0]);
System.out.println(arr[1] + 3);
//遍历
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
System.out.println("第"+(i+1)+"个元素为:"+arr[i]);
}
//for-each
for (int num : arr) {
System.out.println(num);
}
}
}
练习
翻转整数
给定一个 32 位有符号整数,将整数中的数字进行反转。
示例 1:
输入: 123
输出: 321
示例 2:
输入: -123
输出: -321
如果反转后整数溢出那么就返回 0。
demo:
public class ReverseInteger {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int x = 123;
int y = -123;
System.out.println(reverse(x));
System.out.println(reverse(y));
}
//如果反转后整数溢出那么就返回0
public static int reverse(int x) {
int rev = 0;
while (x != 0) {
int pop = x % 10;
x /= 10;
// 检查溢出:如果 rev > Integer.MAX_VALUE/10 或 rev < Integer.MIN_VALUE/10,则会溢出
if (rev > Integer.MAX_VALUE / 10 || (rev == Integer.MAX_VALUE / 10 && pop > Integer.MAX_VALUE % 10)) return 0;
if (rev < Integer.MIN_VALUE / 10 || (rev == Integer.MIN_VALUE / 10 && pop < Integer.MIN_VALUE % 10)) return 0;
rev = rev * 10 + pop;
}
return rev;
}
}
面向对象
基础创建
Person类:
package com.yuy0ung.test06;
/**
* 人类
*/
public class Person {
//特性(属性)
String name;
int age;
double height;
//行为(方法)
//学习的方法
public void study() {
System.out.println("我学,我practice,我每天到晚就酷酷学,我随时库库练!");
}
}
Test测试类:
package com.yuy0ung.test06;
/**
* 测试类
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建Person的对象
Person p1 = new Person();
//对属性赋值
p1.name = "6s6";
p1.age = 18;
p1.height = 170.3;
//读取属性
System.out.println(p1.name);
System.out.println(p1.age);
System.out.println(p1.height);
//调用方法--学习
p1.study();
}
}
构造器
尽量保持空构造器存在(即使默认有隐式创建了构造器)
Person类
package com.yuy0ung.test06;
/**
* 人类
*/
public class Person {
//特性(属性)
String name;
int age;
double height;
//行为(方法)
//学习的方法
public void study() {
System.out.println("我学,我practice,我每天到晚就酷酷学,我随时库库练!");
}
//alt+insert快速添加构造器
//显式编写构造器,不定义返回值
public Person(){
System.out.println("111");
}
//重载构造器
public Person(String name, int age, double height) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.height = height;
}
}
Test02测试类:
package com.yuy0ung.test06;
public class Test02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建Person对象
Person p = new Person();
p.name = "Yuy0ung";
p.age = 18;
p.height = 174.2;
Person p2 = new Person("Yuy0ung的gf", 18, 164.2);
System.out.println(p2.name);
}
}
封装
Girl类
package com.yuy0ung.Test07;
public class Girl {
//属性:
private int age;
//给age提供赋值和读取值的方法
public void setAge(int age) {
if (age > 30) {
this.age = 18;
}
else {
this.age = age;
}
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
}
Test测试类
package com.yuy0ung.Test07;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建对象
Girl g = new Girl();
g.setAge(28);
System.out.println(g.getAge());
}
}
Person类:
package com.yuy0ung.Test07;
public class Person {
private int age;
private String name;
private double height;
//alt+insert快速生成getter和setter
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public double getHeight() {
return height;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void setHeight(double height) {
this.height = height;
}
}
继承
父类Person
package com.yuy0ung.test08;
public class Person {
//父类公共的属性
private String name;
private int age;
private double height;
//构造器,mac是cmd+n
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public double getHeight() {
return height;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public void setHeight(double height) {
this.height = height;
}
//吃饭
public void eat() {
System.out.println("我吃吃吃");
}
//说话
public void speak() {
System.out.println("我说说说");
}
//睡觉
public void sleep() {
System.out.println("zzzZZZ");
}
}
子类Student
package com.yuy0ung.test08;
public class Student extends Person {
//继承父类Person
//定义额外属性、方法
private int sno;
public int getSno() {
return sno;
}
public void setSno(int sno) {
this.sno = sno;
}
public void Study() {
System.out.println("我学学学");
}
}
测试类Test:
package com.yuy0ung.test08;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//定义子类对象
Student s = new Student();
s.setSno(2023122068);
s.setAge(18);
s.setHeight(174.4);
s.setName("Yuy0ung");
s.Study();
s.eat();
s.sleep();
s.speak();
}
}
实现代码复用,多态的基础
方法的重写
Person类:
package com.yuy0ung.test09;
public class Person {
public void eat() {
System.out.println("我吃吃吃");
}
}
继承的学生类:
package com.yuy0ung.test09;
public class Student extends Person {
public void eat() {
System.out.println("我不仅吃,我还喝快哉快哉酒");
}
}
测试类Test:
package com.yuy0ung.test09;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建学生对象
Student s = new Student();
s.eat();
}
}
- 方法重载:在同一类中,同一方法,不同形参列表
- 方法重写:父子类中,子类对父类的方法内容进行重写
多态
用于提高代码扩展性,指的是方法的多态而不是属性,就是不同对象的同名行为的表现状态不同
前提:
- 继承
- 重写
- 父类引用了指向子类的对象(如此调用子类重写的方法)
女孩Girl类:
package com.yuy0ung.test10;
public class Girl {
//玩
public void play(Animal animal) {
animal.shout();
}
}
父类Animal:
package com.yuy0ung.test10;
public class Animal {
//叫
public void shout() {
System.out.println("我叫");
}
}
子类1,Cat:
package com.yuy0ung.test10;
public class Cat extends Animal {
//重写
public void shout() {
System.out.println("喵~");
}
//抓挠
public void scratch() {
System.out.println("挠你!");
}
}
子类2,Dog:
package com.yuy0ung.test10;
public class Dog extends Animal {
//重写
public void shout() {
System.out.println("汪汪");
}
//保安(^_^)
public void guard() {
System.out.println( "我正在看家护院...");
}
}
异常处理
try、catch、finally
package com.yuy0ung.test11;
public class Test01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
//两个数求商
int num1 = 12;
int num2 = 0;
System.out.println("商:" + num1 / num2);
} catch (Exception ex) {
System.out.println("程序错误");
} finally {
System.out.println("始终都会执行finally");
}
}
}
Throw、throws
package com.yuy0ung.test11;
public class Test02 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
devide();
}
//两数相处的方法
public static void devide() throws Exception {
int num1 = 12;
int num2 = 0;
if (num2 == 0) {
//人为制造异常
// try {
// throw new Exception();
// } catch (Exception e) {
// System.out.println("这里用try-catch异常处理");
// }
throw new Exception();
}else {
System.out.println("商:" + num1 / num2);
}
}
}
Throw在方法内部,throws在方法声明处
throw + 异常对象,throws + 异常类型
throw:异常出现的源头,制造异常的地方;throws:在方法声明处声明可能的异常,调用者要么自己处理,要么向外抛出
集合
ArrayList
package com.yuy0ung.test12;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//定义一个集合
ArrayList list = new ArrayList();
System.out.println(list);
//增加元素
list.add("Yuy0ung");
list.add("Yuy1ung");
list.add("Yuy2ung");
list.add("Yuy3ung");
System.out.println(list);
//删除
list.remove("Yuy1ung");
System.out.println(list);
//改
list.set(0, "Yuy4ung");
System.out.println(list);
//查看
System.out.println(list.get(2));
//遍历
for(int i = 0;i < list.size();i++) {
System.out.println(list.get(i));
}
}
}
书店demo
作为快速复习了java基础的一点小实践
菜单
首先完成脚本的菜单栏,用于呈现和选择各种功能点:
package com.yuy0ung.test13;
import java.util.Scanner;
import static javafx.application.Platform.exit;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//打印菜单
while(true) {
System.out.println("这里是Yuy0ung的书店");
System.out.println("1.展示书籍");
System.out.println("2.上架图书");
System.out.println("3.下架图书");
System.out.println("4.退出程序");
System.out.println("请输入想要使用的功能序号");
//键盘录入,使用scanner类
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
//录入序号
int choice = scanner.nextInt();
if (choice == 1) {
System.out.println("------展示书籍:");
} else if (choice == 2) {
System.out.println("------上架图书:");
} else if (choice == 3) {
System.out.println("------下架图书:");
} else if (choice == 4) {
System.out.println("------退出");
break;
}
}
}
}
功能点完善
创建一个书籍Book类:
package com.yuy0ung.test13;
public class Book {
//属性
private int bId;
private String bName;
private String bAuthor;
public int getbId() {
return bId;
}
public String getbName() {
return bName;
}
public String getbAuthor() {
return bAuthor;
}
public void setbId(int bId) {
this.bId = bId;
}
public void setbName(String bName) {
this.bName = bName;
}
public void setbAuthor(String bAuthor) {
this.bAuthor = bAuthor;
}
public Book(int bId, String bName, String bAuthor) {
this.bId = bId;
this.bName = bName;
this.bAuthor = bAuthor;
}
public Book() {
}
}
然后完善Test方法:
package com.yuy0ung.test13;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Scanner;
import static javafx.application.Platform.exit;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList books = new ArrayList();//用于存储书籍的数组
//打印菜单
while(true) {
System.out.println("这里是Yuy0ung的书店");
System.out.println("1.展示书籍");
System.out.println("2.上架图书");
System.out.println("3.下架图书");
System.out.println("4.退出程序");
System.out.println("请输入想要使用的功能序号");
//键盘录入,使用scanner类
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
//录入序号
int choice = scanner.nextInt();
if (choice == 1) {
System.out.println("------展示书籍:");
for(int i = 0; i < books.size(); i++) {
Book book = (Book) books.get(i);
System.out.println(book.getbId()+"---"+book.getbName()+"---"+book.getbAuthor());
}
} else if (choice == 2) {
System.out.println("------上架图书:");
System.out.println("请输入书籍编号:");
int bId = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.println("请输入书籍名称");
String bName = scanner.next();
System.out.println("请输入书籍作者");
String bAuthor = scanner.next();
//创建书籍对象
Book book = new Book(bId, bName, bAuthor);
books.add(book);//添加书籍进入集合
} else if (choice == 3) {
System.out.println("------下架图书:");
System.out.println("输入删除书籍编号");
int delId = scanner.nextInt();
//删除
for(int i = 0; i < books.size(); i++) {
Book book = (Book) books.get(i);
if(book.getbId() == delId) {
books.remove(i);
}
}
} else if (choice == 4) {
System.out.println("------退出");
break;
}
}
}
}
完成
I/O流
输入输出(相对于程序而言)
流的类型很多:
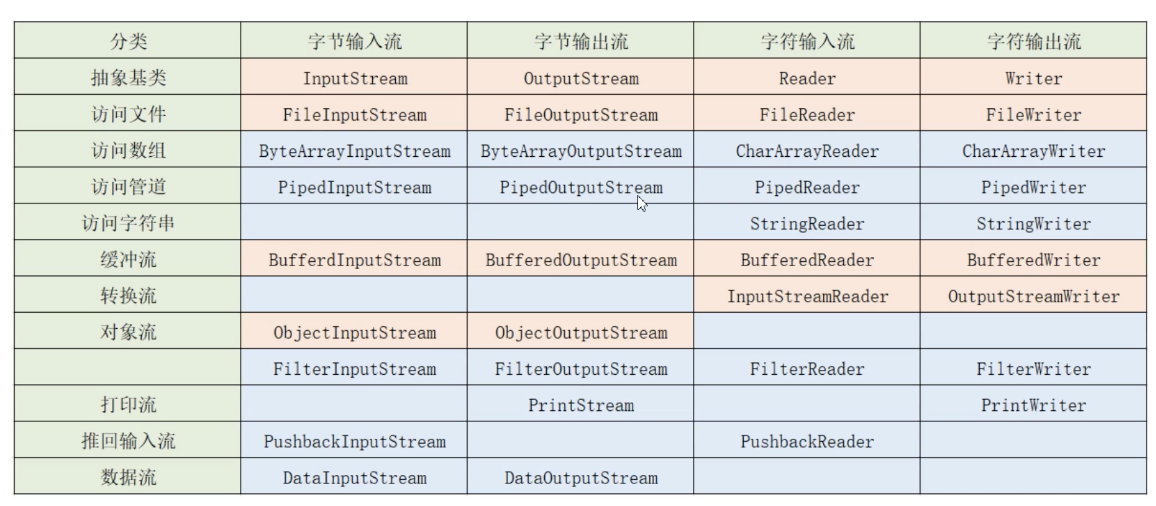
大同小异
文件字符输入流
从txt读字符串
package com.yuy0ung.test14;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Test01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//对文件进行封装为File类对象
File file = new File("/Users/yuy0ung/1.txt");
//输入输出(字符)流
FileReader fr = new FileReader(file);
//读,循环
int n1 = fr.read();
while (n1 != -1) {
System.out.println(n1);
n1 = fr.read();
}
//关闭流
fr.close();
}
}
文件字符输出流
字符串写入文件
package com.yuy0ung.test14;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Test02 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String str = "Yuy0ung你好";
//文件
File file = new File("/Users/yuy0ung/2.txt");
//字符输出流
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter(file);
//输出
fw.write(str);
//关闭
fw.close();
}
}
书店demo2
上面的书店使用数组存储数据,但是这样没有办法永久保存,程序一旦关闭,数据就会丢失,此时就可以运用I/O流将文件数据存储进文件
选定对象流:
- FileInputStream
- FileOutputStream
- ObjectInputStream
- ObjectOutputStream
还需要序列化,实现了Serializable接口才具备将对象输出到文件的能力:
Implements Serializable
Test类:
package com.yuy0ung.test15;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
//打印菜单
while(true) {
System.out.println("这里是Yuy0ung的书店");
System.out.println("1.展示书籍");
System.out.println("2.上架图书");
System.out.println("3.下架图书");
System.out.println("4.退出程序");
System.out.println("请输入想要使用的功能序号");
//键盘录入,使用scanner类
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
//录入序号
int choice = scanner.nextInt();
if (choice == 1) {
System.out.println("------展示书籍:");
//从文件读取
File file = new File("/Users/yuy0ung/books.txt");
//判断文件是否存在
if(file.exists() == true) {
//存在
//输入流
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file);
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(fis);
//读取集合
ArrayList books = (ArrayList)(ois.readObject());
for(int i = 0; i < books.size(); i++) {
Book book = (Book) books.get(i);
System.out.println(book.getbId()+"---"+book.getbName()+"---"+book.getbAuthor());
}
}else {
System.out.println("未上新书籍,请先上新书籍");
}
} else if (choice == 2) {
System.out.println("------上架图书:");
System.out.println("请输入书籍编号:");
int bId = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.println("请输入书籍名称");
String bName = scanner.next();
System.out.println("请输入书籍作者");
String bAuthor = scanner.next();
//创建书籍对象
Book book = new Book(bId, bName, bAuthor);
//从文件读取
File file = new File("/Users/yuy0ung/books.txt");
//判断文件是否存在
if(file.exists() == true) {
//存在
//输入流
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file);
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(fis);
//读取集合
ArrayList books = (ArrayList)(ois.readObject());
//追加书籍
books.add(book);
//写入文件
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(file);
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(fos);
//写出
oos.writeObject(books);
//关闭流
oos.close();
}else {
ArrayList books = new ArrayList();//用于存储书籍的数组
books.add(book);//添加书籍进入集合
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(file);
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(fos);
//写出
oos.writeObject(books);
//关闭流
oos.close();
}
} else if (choice == 3) {
System.out.println("------下架图书:");
System.out.println("输入删除书籍编号");
int delId = scanner.nextInt();
//读取
File file = new File("/Users/yuy0ung/books.txt");
//输入流
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file);
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(fis);
//读取集合
ArrayList books = (ArrayList)(ois.readObject());
//删除
for(int i = 0; i < books.size(); i++) {
Book book = (Book) books.get(i);
if(book.getbId() == delId) {
books.remove(i);
}
}
//写入
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(file);
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(fos);
//写出
oos.writeObject(books);
//关闭流
oos.close();
} else if (choice == 4) {
System.out.println("------退出");
break;
}
}
}
}
给Book类加上serializable接口:
package com.yuy0ung.test15;
import java.io.Serializable;
public class Book implements Serializable {
//属性
private int bId;
private String bName;
private String bAuthor;
public int getbId() {
return bId;
}
public String getbName() {
return bName;
}
public String getbAuthor() {
return bAuthor;
}
public void setbId(int bId) {
this.bId = bId;
}
public void setbName(String bName) {
this.bName = bName;
}
public void setbAuthor(String bAuthor) {
this.bAuthor = bAuthor;
}
public Book(int bId, String bName, String bAuthor) {
this.bId = bId;
this.bName = bName;
this.bAuthor = bAuthor;
}
public Book() {
}
}
多线程
继承thread类
实现runnable接口
实现callable接口
这里简单实现一下继承的:
Test类:
package com.yuy0ung.test16;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//主线程的任务
for(int i = 1; i <= 20; i++) {
System.out.println("main--------"+i);
}
//创建子线程对象
TestThread t1 = new TestThread();
//启动线程
t1.start();//启动会和主线程争抢资源
for(int i = 1; i <= 20; i++) {
System.out.println("main---main--"+i);
}
}
}
子线程TestThread类:
package com.yuy0ung.test16;
/**
* 线程类
*/
public class TestThread extends Thread {
//线程对应任务放进一个方法
@Override
public void run() {
//输出10个数
for (int i = 1; i < 20; i++) {
System.out.println("zixiancheng------"+i);
}
}
}
网络编程
socket套接字
链接应用层和传输层,实现客户端和服务端的通信
客户端:
package com.yuy0ung.test17;
import java.io.*;
import java.net.Socket;
public class TestClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
System.out.println("client start");
//套接字:指定服务器IP端口号
Socket s = new Socket("192.168.51.2", 8001);
//输出流传输数据
OutputStream os = s.getOutputStream();
DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream(os);
//传输数据:
dos.writeUTF("hello");
//接受响应
InputStream is = s.getInputStream();
DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream(is);
//输出
String str = dis.readUTF();
System.out.println("Server:"+str);
//流、网络资源关闭
dos.close();
s.close();
}
}
服务端:
package com.yuy0ung.test17;
import java.io.*;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
public class TestServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
System.out.println("Server start...");
// 套接字
ServerSocket ss = new ServerSocket(8001);
//等待客户端发送数据
Socket s = ss.accept();
// 输入流
InputStream is = s.getInputStream();
DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream(is);
// 接受client数据
String str = dis.readUTF();
System.out.println("client:"+str);
//响应
OutputStream os = s.getOutputStream();
DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream(os);
dos.writeUTF("copy that");
//关闭
dos.close();
dis.close();
s.close();
ss.close();
}
}
XML
基本样式:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?>
<!--
注释:
verison:版本号
encoding:文档编码信息
-->
<student>
<student id="1">
<name>Yuy0ung</name>
<sex>男</sex>
<age>19</age>
</student>
<student id="2">
<name>fpc</name>
<sex>男</sex>
<age>20</age>
</student>
<student id="3">
<name>ljc</name>
<sex>男</sex>
<age>20</age>
</student>
</student>
注解
package com.yuy0ung.test19;
/**
* @author Yuy0ung
* @version 1.0
*/
public class Test {
/**
*
* @param a 求和第一个变量
* @param b 求和第二个变量
* @return 返回值
*/
public int add(int a, int b) {
return a + b;
}
}
重写:
package com.yuy0ung.test19;
public class Person {
public void eat() {
System.out.println("eat");
}
}
override
package com.yuy0ung.test19;
public class Student extends Person {
@Override
public void eat() {
super.eat();
}
}